helm 详解及实践应用全集
一、Helm 概述
Helm 是 Kubernetes 的一个包管理工具,类似于 Linux 下的包管理工具如 yum、apt 等。可以方便的将之前打包好的 yaml 文件部署到 Kunernetes 上。
在 Helm 中有三个主要概念:
| 概念 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| helm | 一个命令行工具,主要用于 k8s 应用 Chart 的创建、打包、发布和管理。 |
| Chart | 应用描述,它是一系列用于描述 k8s 资源相关文件的集合(可以理解为 yaml 的集合)。 |
| Release | 基于 Chart 的部署实体,一个 Chart 被 Helm 运行后将会生成一个对应的 release,然后将在 k8s 中创建出真正运行的资源对象,它是一个应用级别的版本管理。 |
基于 Chart 的部署实体,一个 Chart 被 Helm 运行后将会生成一个对应的 release,然后将在 k8s 中创建出真正运行的资源对象,它是一个应用级别的版本管理。 在 2019 年 11 月 13日,Helm 团队发布了稳定版本Helm v3,这也是当前主流版本。该版本与往期版本相比较有主要以下变化:
删除了 Tiller;
支持 release 在不同命名空间中重用;
支持直接将 Chart 推送到 docker 仓库中
v3 之前版本架构

v3 版本架构
Helm官网:
Helm插件:
https://helm.sh/zh/docs/community/related/
二、Helm 部署安装
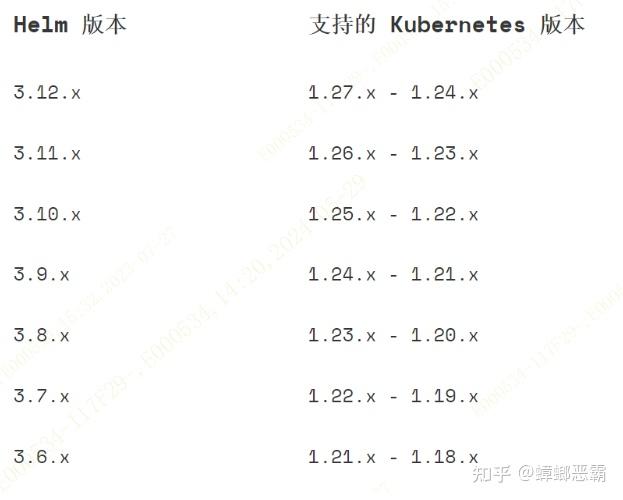
1)版本选择及下载安装
由于集群版本选择1.24版本,考虑后续兼容,选择3.12.x版本的helm
国内下载地址:
https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/helm/v3.12.0/
使用命令下载:
wget https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/helm/v3.12.0/helm-v3.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && tar -xvf helm-v3.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && cp linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/
2)基础配置
A)配置公有仓库
配置国内Chart仓库
阿里云仓库(https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts )
helm repo add stable http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/chartshelm repo add aliyun https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts helm repo add tkemarket https://market-tke.tencentcloudcr.com/chartrepo/opensource-stable helm repo update helm repo list
添加腾讯云镜像helm chart 仓库
helm repo add $instance-$namespace https://$instance.tencentcloudcr.com/chartrepo/$namespace --username $username --password $instance-token
B)连接集群
配置kubectl ,及 ~/.kube/config
chmod g-rw ~/.kube/configchmod o-r ~/.kube/config
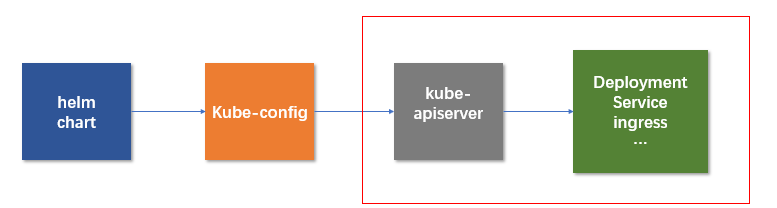
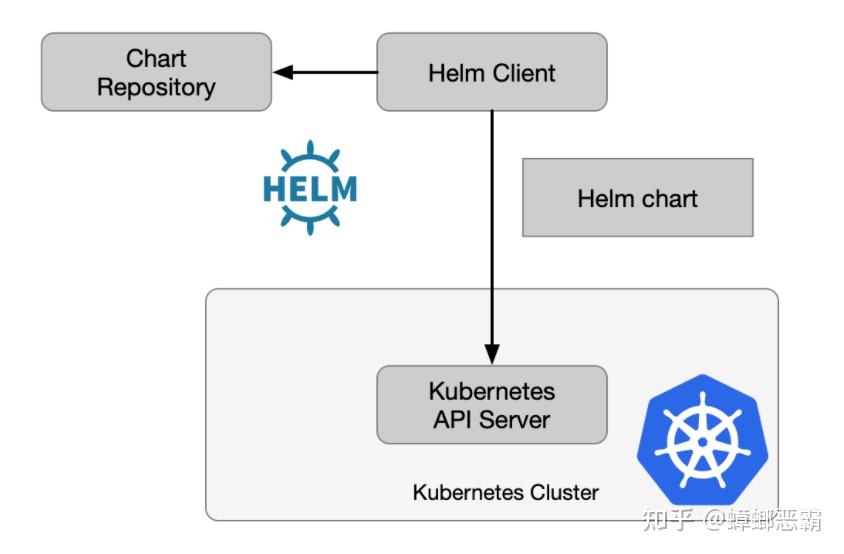
Helm v3对比 Helm v2已移除 Tiller 组件,Helm 客户端可直接连接集群的 ApiServer,应用相关的版本数据直接存储在 Kubernetes 中。如下图所示:
参考腾讯云文档:
https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/1141/41944注:
使用 Helm CLI 上传 Chart 包需要安装 helm-push 插件,该插件支持使用 helm push 指令推送 helm chart 至指定 repo,同时支持上传目录及压缩包。
helm plugin install https://github.com/chartmuseum/helm-push
安装插件后需要使用插件进行上传例如:【仓库不存在只是展示写法】
helm cm-push kafka-28.2.1.tgz kafka/common-job
C)安装插件
插件使用 $ helm plugin install <path|url> 命令安装插件。你可以在本地文件系统上传一个路径或远程仓库url给插件。The helm plugin install 命令会克隆或拷贝给定路径的插件到 $HELM_PLUGINS。
$ helm plugin install https://github.com/adamreese/helm-env
如果是插件tar包,仅需解压插件到$HELM_PLUGINS目录。也可以用tar包的url直接安装: helm plugin install https://domain/path/to/plugin.tar.gz。
插件安装说明官方文档:Helm插件指南
可以使用helm env 命令查看插件目录
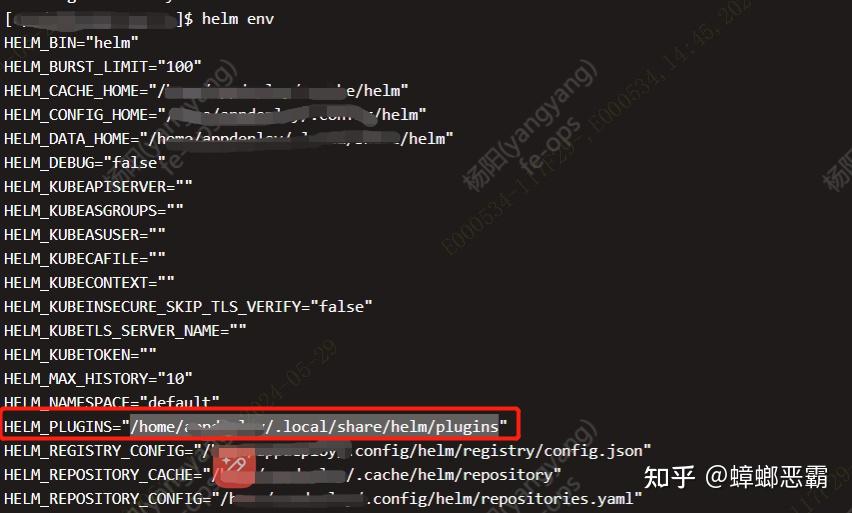
在插件安装目录会找到插件的目录,以及目录bin目录下的二机制执行文件

实例安装
Dashboard 插件安装
国内镜像地址: https://hub.nuaa.cf/komodorio/helm-dashboard
推荐二进制安装: helm plugin install https://github.com/komodorio/helm-dashboard.git
【因为网络问题会无法安装,可以使用国内地址】
三、Helm 应用落地
1)工作流程简诉
以下是Helm的工作流程
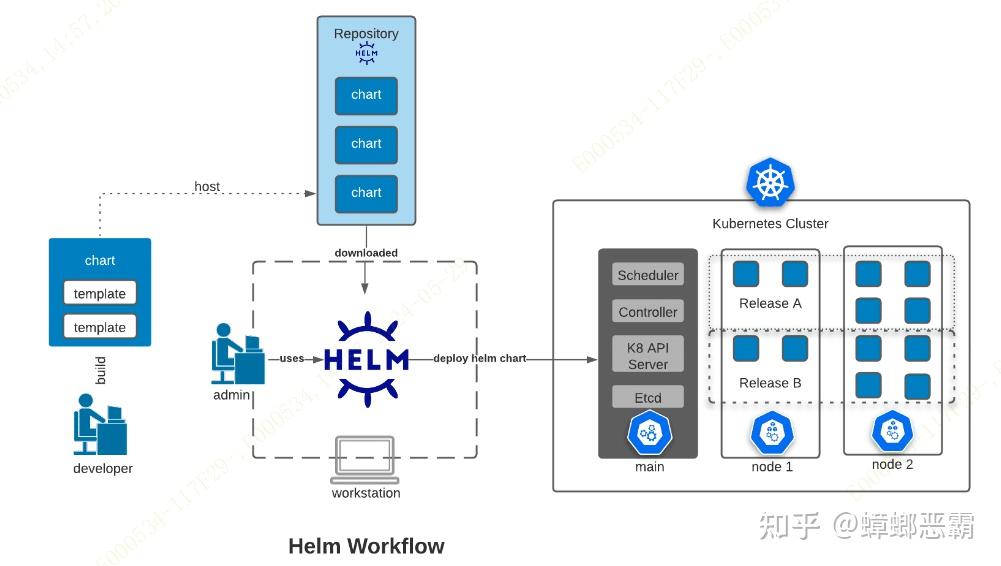
简诉如下:
helm install my-work -n my-namespace my-work/ helm install my-work -n my-namespace my-company/my-work
helm : 工具
my-work : 需要安装的服务
my-work/ 或 my-company/my-work : chart包
2) Charts 包结构及使用简诉
以下内容为参考:Helm入门(一篇就够了)-阿里云开发者社区
使用helm create命令创建一个新的Chart,Chart目录包含描述应用程序的文件和目录,包括Chart.yaml、values.yaml、templates目录等;
A)创建Charts 包
在本地机器上使用helm create命令创建一个名为wordpress的Chart:
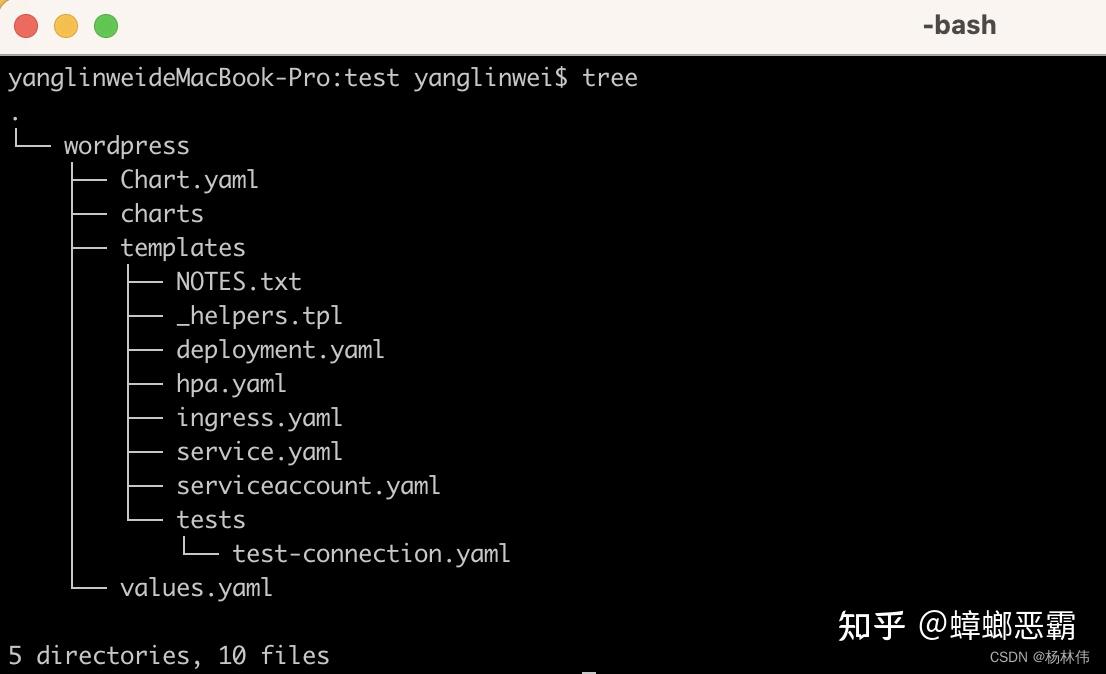
B)Charts 目录
在当前文件夹,可以看到创建了一个wordpress的目录,且里面的内容如下:
创建/编辑Chart配置
使用编辑器编辑Chart配置文件,包括Chart.yaml和values.yaml。
C) Chart.yaml
Chart.yaml包含Chart的元数据和依赖项
Chart.yaml的模板及注释如下:
apiVersion: chart API 版本 (必需) #必须有name: chart名称 (必需) # 必须有 version: 语义化2 版本(必需) # 必须有kubeVersion: 兼容Kubernetes版本的语义化版本(可选)description: 一句话对这个项目的描述(可选)type: chart类型 (可选)keywords: - 关于项目的一组关键字(可选)home: 项目home页面的URL (可选)sources: - 项目源码的URL列表(可选)dependencies: # chart 必要条件列表 (可选) - name: chart名称 (nginx) version: chart版本 ("1.2.3") repository: (可选)仓库URL ("https://example.com/charts") 或别名 ("@repo-name") condition: (可选) 解析为布尔值的yaml路径,用于启用/禁用chart (e.g. subchart1.enabled ) tags: # (可选) - 用于一次启用/禁用 一组chart的tag import-values: # (可选) - ImportValue 保存源值到导入父键的映射。每项可以是字符串或者一对子/父列表项 alias: (可选) chart中使用的别名。当你要多次添加相同的chart时会很有用maintainers: # (可选) # 可能用到 - name: 维护者名字 (每个维护者都需要) email: 维护者邮箱 (每个维护者可选) url: 维护者URL (每个维护者可选)icon: 用做icon的SVG或PNG图片URL (可选)appVersion: 包含的应用版本(可选)。不需要是语义化,建议使用引号deprecated: 不被推荐的chart (可选,布尔值)annotations: example: 按名称输入的批注列表 (可选).举例:
name: nginx-helm apiVersion: v1 version: 1.0.0
D ) values.yaml
values.yaml包含应用程序的默认配置值,举例:
image: repository: nginx tag: '1.19.8'
E) templates
在模板中引入values.yaml里的配置,在模板文件中可以通过 .VAlues对象访问到,例如:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-helm-{{ .Values.image.repository }}
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-helm
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-helm
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-helm
image: {{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag }}
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCPE) 打包Chart
使用helm package命令将Chart打包为一个tarball文件,例如在wordpress目录中使用helm package命令将Chart打包为一个tarball文件:
helm package wordpress/
这将生成一个名为wordpress-0.1.0.tgz的tarball文件。
F) 上传 Chart
将打包好的Chart发布到一个Helm Repository中。可以使用helm repo add命令添加一个Repository,然后使用helm push命令将Chart推送到Repository中,例如:
helm repo add myrepo https://example.com/charts helm push wordpress-0.1.0.tgz myrepo
G) 安装 Release
使用helm install命令安装Chart的Release,可以通过命令行选项或指定values.yaml文件来配置Release,例如:
helm install mywordpress myrepo/wordpress
这将在Kubernetes集群中创建一个名为mywordpress的Release,包含WordPress应用程序和MySQL数据库。
H) 更新 Release
使用helm upgrade 命令查看当前运行的Release ,例如:
helm upgrade mywordpress myrepo/wordpress --set image.tag=5.7.3-php8.0-fpm-alpine
3) Charts 语法详述
A) 使用语法使用双花括号 {{ }}
B) 引用内置对象
前面提到过可以在模板中使用 {{ .Release.Name }} 获取 release 的名称,Release 是模板中可以访问的几个顶级对象之一:
Release:该对象描述了 release 本身的相关信息Release.Name:release 名称Release.Namespace:release 安装到的命名空间Release.IsUpgrade:如果当前操作是升级或回滚,是为 trueRelease.IsInstall:如果当前操作是否是安装,是为 trueRelease.Revision:release 的 revision 版本号,在安装时为1,每次升级或回滚都会+1Release.Service:渲染当前模板的服务,在 Helm 上,实际上该值始终为 Helm
Values:从values.yaml文件和用户提供的 values 文件传递到模板的 Values 值Chart:获取Chart.yaml文件的内容,该文件中的任何数据都可以访问Files:可以访问 chart 中的所有非特殊文件,虽然无法使用它来访问模板文件,但是可以来访问 chart 中的其他文件。Files.Get:用于根据名称获取文件(比如.Files.Get config.ini)Files.GetBytes:用于以 bytes 数组而不是字符串的形式来获取文件内容的函数Files.Glob:用于返回名称于给定的 shell glob 模式匹配的文件列表Files.Lines:可以逐行读取文件的函数,对于遍历文件中的每行内容很有用Files.AsSecrets:将文件内容以 Base64 编码的字符串返回的函数Files.AsConfig:将文件正文作为 YAML 字典返回的函数
Capabilities:获取有关 Kubernetes 集群的信息的对象Capabilities.APIVersions:支持的版本集合Capabilities.APIVersions.Has $version:判断一个版本(比如batch/v1)或资源(比如apps/v1/Deployment)是否可用Capabilities.Kube.Version:Kubernetes 的版本Capabilities.Kube:是 Kubernetes 版本的缩写Capabilities.Kube.Major:Kubernetes 主版本Capabilities.Kube.Minor:Kubernetes 的次版本
Template:当前正在执行的模板的相关信息Name:当前模板的命名空间文件路径(比如mychart/templates/mytemplate.yaml)BasePath:当前 chart 的模板目录的命名空间路径(比如mychart/templates)
更多具体用法可以参考官方文档:
https://helm.sh/zh/docs/howto/charts_tips_and_tricks/
C) 使用管道 及 函数
模板语言有一个强大的功能就是管道(Pipeline),它可以将一系列模板命令链接在一起,一起对外提供服务
Helm 有60多种可用的函数,其中一些是由 Go 模板语言本身定义的,其他大多数都是 Sprig 模板库提供的,一般常用的也就是 Spig 模板库的函数 。
另外需要注意的是:在模板中,运算符(eq、ne、lt、gt、and、or 等等)均实现为函数,在管道中,运算符可以用括号()进行分割。
想要使用更多函数,可以查看文档:
https://masterminds.github.io/sprig/
# chartdemo/templates/configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-ConfigMap
data:
# default 函数,设置默认值
DefaultFunc1: {{ .Values.name | default "abc" }}
DefaultFunc2: {{ .Values.app | default "abc" }}
# upper 函数,转换成大写
UpperFunc: {{ .Values.name | default "abc" | upper }}
# quote 函数,加引号
QuoteFunc: {{ .Values.name | quote }}
# repeat 函数,重复数据
RepeatFunc: {{ .Values.name | repeat 5 }}D) 控制语句
条件语句:
{{ if eq .Values.enableService true }}
kind: Service
{{ end }}循环:
{{ range $index, $value := .Values.envVars }}
- name: {{ $value.name }}
value: {{ $value.value }}
{{- end }}E ) 变量
定义变量的方法有点类似 Golang 中的定义方法,只是需要一个$符号前缀
变量的使用频率较低,但可以用他们来简化代码,以及更好地使用with和range
在 with 下面是用的作用域里面的值还是外部的值。为了解决这个问题,就需要使用变量来进行改进
apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: {{ .Release.Name }}-ConfigMapdata: {{- $releaseName := .Release.Name }} {{- with .Values }} releaseName: {{ $releaseName }} name: {{ .name }} {{- end }}apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: {{ .Release.Name }}-ConfigMapdata: |- # 数组遍历 {{- range $index, $value := .Values.sports }} {{ $index }}:{{ $value }}
{{- end }} # 对象遍历 {{- range $index, $data := .Values.language }} {{- range $k, $v := $data }} {{ $k }}: {{ $v }} {{- end }} {{- end }}F)访问文件
有时候需要导入一个不是模板的文件并注入其内容,此时就需要用到 .Files。
Helm 提供了一个 .Files 对象对文件的访问,但在使用之前需要注意:
可以在 Helm chart 中添加额外的文件,但这些文件也会被打包,由于 Kubernetes 对象的存储限制,Charts 必须小于 1M
由于一些安全原因,通过
.Files对象无法访问某些文件无法访问
templates/下面的文件无法访问使用
.helmignore排除的文件Chart 不会保留 UNIX 模式的信息,所以,当使用
.Files对象时,文件级别的权限不会对文件的可用性产生影响。读取三个文件:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}-ConfigMap
data:
{{- $files := .Files }}
{{- range tuple "f1.conf" "f2.conf" "f3.conf" }}
{{ . }}: |-
{{ $files.Get . }}
{{- end }}结果:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: mychart-1576046462-ConfigMap data: f1.conf: |- message = 1 f2.conf: |- message = 2 f3.conf: |- message = 3
G)模板
_ 开头的这些文件其实就是 Helm 中的 partials 文件,所以我们完全可以将命名模板定义在这些 partials 文件中,默认就是 _helpers.tpl 文件。
通过 define 创建命名模板:
{{ define "MY.NAME" }}
# 模板内容区域
{{ end }}示例:
# chartdemo/templates/configmap.yaml
{{ define "chartdemo.labels" }}
labels:
app: nginx
author: {{ .Values.name }}
{{ end }}
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: myapp
{{- template "chartdemo.labels" -}}
data:
key: valuetemplate 只能导入同文件:
{{ template "chartdemo.labels" . }}导入【多种】:
{{ include "chartdemo.labels" . | indent 2 }}在数据前面空两个格,实现数据 YAML 格式的合法性。通常在使用中也是推荐使用 include 而不是 template。
H ) NOTES.txt
在 chart 安装或者升级结束时,Helm 可以为用户打印出一些有用的信息,使用模板也可以自定义这些信息。
要将安装说明添加到 chart 中,只需要创建一个 templates/NOTES.txt 文件,该文件纯文本的,但是可以像模板一样进行处理,并具有所有常规模板的功能和可用对象。
Thank you for installing {{ .Chart.Name }}.
Your release is named {{ .Release.Name }}.
To learn more about the release, try:
$ helm status {{ .Release.Name }}
$ helm get {{ .Release.Name }}4) 单个微服务Charts 包的详述与例析
A) 文件结构
微服务的构建一般我们需要以下的文件:
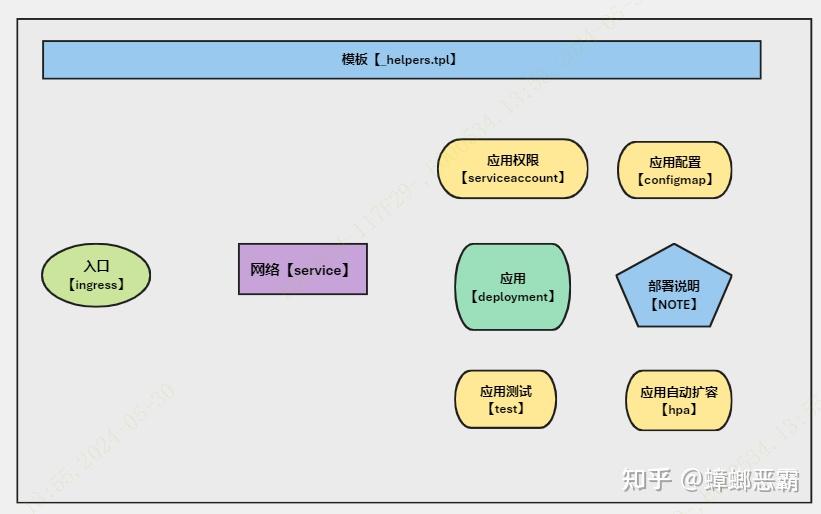
xxx-service/ |-- charts |-- Chart.yaml |-- templates | |-- deployment.yaml | |-- _helpers.tpl | |-- hpa.yaml | |-- ingress.yaml | |-- comfigmap.yaml | |-- NOTES.txt | |-- serviceaccount.yaml | |-- service.yaml | `-- tests `-- values.yaml
| Chart.yaml |
|---|
apiVersion: v2 name: xxx-service description: A Helm for TKE xxx-service # A chart can be either an 'application' or a 'library' chart. # # Application charts are a collection of templates that can be packaged into versioned archives # to be deployed. # # Library charts provide useful utilities or functions for the chart developer. They're included as # a dependency of application charts to inject those utilities and functions into the rendering # pipeline. Library charts do not define any templates and therefore cannot be deployed. type: application # This is the chart version. This version number should be incremented each time you make changes # to the chart and its templates, including the app version. # Versions are expected to follow Semantic Versioning (https://semver.org/) version: 2024.05.0005 # This is the version number of the application being deployed. This version number should be # incremented each time you make changes to the application. Versions are not expected to # follow Semantic Versioning. They should reflect the version the application is using. # It is recommended to use it with quotes. appVersion: "V1.1"
| values.yaml |
|---|
# Default values for canna-admin.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare variables to be passed into your templates.
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: xxx.com/xxxx/xxxxx-service
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Overrides the image tag whose default is the chart appVersion.
tag: "V1.1"
imagePullSecrets: registrysecret
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: false
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# The name of the service account to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name: ""
podAnnotations: {}
podSecurityContext: {}
# fsGroup: 2000
securityContext: {}
# capabilities:
# drop:
# - ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsUser: 1000
service:
type: LoadBalancer # ClusterIP
port: 1234
envconfig:
envname: xxxxx-service-env
env:
TZ: Asia/Shanghai
ingress:
enabled: false
className: ""
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
hosts:
- host: chart-example.local
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls: []
# - secretName: chart-example-tls
# hosts:
# - chart-example.local
resources:
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 2048Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1024Mi
autoscaling:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 100
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80
# targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage: 80
security:
groupid: xxxxx
nodeSelector: {
xxxxxx: xxxxx
}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}| _helpers.tpl |
|---|
{{/*
Expand the name of the chart.
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.name" -}}
{{- default .Chart.Name .Values.nameOverride | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" }}
{{- end }}
{{/*
Create a default fully qualified app name.
We truncate at 63 chars because some Kubernetes name fields are limited to this (by the DNS naming spec).
If release name contains chart name it will be used as a full name.
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.fullname" -}}
{{- if .Values.fullnameOverride }}
{{- .Values.fullnameOverride | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" }}
{{- else }}
{{- $name := default .Chart.Name .Values.nameOverride }}
{{- if contains $name .Release.Name }}
{{- .Release.Name | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" }}
{{- else }}
{{- printf "%s-%s" .Release.Name $name | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{/*
Create chart name and version as used by the chart label.
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.chart" -}}
{{- printf "%s-%s" .Chart.Name .Chart.Version | replace "+" "_" | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" }}
{{- end }}
{{/*
Common labels
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.labels" -}}
helm.sh/chart: {{ include "app-server.chart" . }}
{{ include "app-server.selectorLabels" . }}
{{- if .Chart.AppVersion }}
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ .Chart.AppVersion | quote }}
{{- end }}
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service }}
{{- end }}
{{/*
Selector labels
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.selectorLabels" -}}
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ include "app-server.name" . }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name }}
{{- end }}
{{/*
Create the name of the service account to use
*/}}
{{- define "app-server.serviceAccountName" -}}
{{- if .Values.serviceAccount.create }}
{{- default (include "app-server.fullname" .) .Values.serviceAccount.name }}
{{- else }}
{{- default "default" .Values.serviceAccount.name }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}| deployment.yaml |
|---|
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}
labels:
k8s.kuboard.cn/layer: svc
{{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
{{- if not .Values.autoscaling.enabled }}
replicas: {{ .Values.replicaCount }}
{{- end }}
selector:
matchLabels:
{{- include "app-server.selectorLabels" . | nindent 6 }}
template:
metadata:
annotations:
eks.tke.cloud.tencent.com/security-group-id: {{ .Values.security.groupid }}
labels:
{{- include "app-server.selectorLabels" . | nindent 8 }}
spec:
serviceAccountName: {{ include "app-server.serviceAccountName" . }}
imagePullSecrets:
- name: registrysecret
volumes:
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
- name: xxxx-xxxx-logs
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: xxxxx-xxxx-logs
securityContext:
{{- toYaml .Values.podSecurityContext | nindent 8 }}
containers:
- name: {{ .Chart.Name }}
securityContext:
{{- toYaml .Values.securityContext | nindent 12 }}
image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag | default .Chart.AppVersion }}"
imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }}
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","/app/springboot.sh stop app.jar >> /app/logs/catalina.out && sleep 60s"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /app/config/bootstrap.properties
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
readOnly: true
subPath: bootstrap.properties
- mountPath: /app/config/logback.xml
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
readOnly: true
subPath: logback.xml
- mountPath: /app/logs
name: xxxx-xxxx-logs
subPathExpr: $(POD_NAME)_$(POD_IP)
env:
{{- range $key, $val := .Values.env }}
- name: {{$key}}
value: {{$val|quote}}
{{- end}}
- name: JAVA_HOME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: JAVA_HOME
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
- name: JAVA_OPTS
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: JAVA_OPTS
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
- name: SW_AGENT_COLLECTOR_BACKEND_SERVICES
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: SW_AGENT_COLLECTOR_BACKEND_SERVICES
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
- name: SW_AGENT_NAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
key: SW_AGENT_NAME
name: {{ .Values.envconfig.envname }}
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: {{ .Values.service.port }}
protocol: TCP
#livenessProbe:
# httpGet:
# path: /
# port: http
#readinessProbe:
# httpGet:
# path: /
# port: http
resources:
requests:
{{- with .Values.resources.requests }}
cpu: {{ .cpu |quote}}
memory: {{ .memory |quote}}
{{- end}}
limits:
{{- with .Values.resources.limits }}
cpu: {{ .cpu |quote}}
memory: {{ .memory |quote}}
{{- end}}
{{- with .Values.nodeSelector }}
nodeSelector:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- with .Values.affinity }}
affinity:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- with .Values.tolerations }}
tolerations:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}| service.yaml |
|---|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
allocateLoadBalancerNodePorts: true
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
type: {{ .Values.service.type }}
ports:
- name: {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}
port: {{ .Values.service.port }}
protocol: TCP
targetPort: {{ .Values.service.port }}
selector:
{{- include "app-server.selectorLabels" . | nindent 4 }}| serviceaccount.yaml |
|---|
{{- if .Values.serviceAccount.create -}}
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: {{ include "app-server.serviceAccountName" . }}
labels:
{{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
{{- with .Values.serviceAccount.annotations }}
annotations:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 4 }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}| ingress.yaml |
|---|
{{- if .Values.ingress.enabled -}}
{{- $fullName := include "app-server.fullname" . -}}
{{- $svcPort := .Values.service.port -}}
{{- if and .Values.ingress.className (not (semverCompare ">=1.18-0" .Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion)) }}
{{- if not (hasKey .Values.ingress.annotations "kubernetes.io/ingress.class") }}
{{- $_ := set .Values.ingress.annotations "kubernetes.io/ingress.class" .Values.ingress.className}}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- if semverCompare ">=1.19-0" .Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion -}}
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
{{- else if semverCompare ">=1.14-0" .Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion -}}
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
{{- else -}}
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
{{- end }}
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: {{ $fullName }}
labels:
{{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
{{- with .Values.ingress.annotations }}
annotations:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 4 }}
{{- end }}
spec:
{{- if and .Values.ingress.className (semverCompare ">=1.18-0" .Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion) }}
ingressClassName: {{ .Values.ingress.className }}
{{- end }}
{{- if .Values.ingress.tls }}
tls:
{{- range .Values.ingress.tls }}
- hosts:
{{- range .hosts }}
- {{ . | quote }}
{{- end }}
secretName: {{ .secretName }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
rules:
{{- range .Values.ingress.hosts }}
- host: {{ .host | quote }}
http:
paths:
{{- range .paths }}
- path: {{ .path }}
{{- if and .pathType (semverCompare ">=1.18-0" $.Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion) }}
pathType: {{ .pathType }}
{{- end }}
backend:
{{- if semverCompare ">=1.19-0" $.Capabilities.KubeVersion.GitVersion }}
service:
name: {{ $fullName }}
port:
number: {{ $svcPort }}
{{- else }}
serviceName: {{ $fullName }}
servicePort: {{ $svcPort }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}| NOTES.txt |
|---|
1. Get the application URL by running these commands:
{{- if .Values.ingress.enabled }}
{{- range $host := .Values.ingress.hosts }}
{{- range .paths }}
http{{ if $.Values.ingress.tls }}s{{ end }}://{{ $host.host }}{{ .path }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- else if contains "NodePort" .Values.service.type }}
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }})
export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")
echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT
{{- else if contains "LoadBalancer" .Values.service.type }}
NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status of by running 'kubectl get --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} svc -w {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}'
export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }} --template "{{"{{ range (index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0) }}{{.}}{{ end }}"}}")
echo http://$SERVICE_IP:{{ .Values.service.port }}
{{- else if contains "ClusterIP" .Values.service.type }}
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} -l "app.kubernetes.io/name={{ include "app-server.name" . }},app.kubernetes.io/instance={{ .Release.Name }}" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
export CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} $POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use your application"
kubectl --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:$CONTAINER_PORT
{{- end }}| hpa.yaml |
|---|
{{- if .Values.autoscaling.enabled }}
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: {{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}
minReplicas: {{ .Values.autoscaling.minReplicas }}
maxReplicas: {{ .Values.autoscaling.maxReplicas }}
metrics:
{{- if .Values.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage }}
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
targetAverageUtilization: {{ .Values.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage }}
{{- end }}
{{- if .Values.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage }}
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
targetAverageUtilization: {{ .Values.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}| test.yaml |
|---|
test 测试用以测试测试是否正常,可以使用busybox 等容器的curl,wget,telnet 等命令去测试端口或基础功能的正常
apiVersion: v1kind: Podmetadata: name: "{{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}-test-connection" labels: {{- include "app-server.labels" . | nindent 4 }} annotations: "helm.sh/hook": testspec: containers: - name: wget image: busybox command: ['wget'] args: ['{{ include "app-server.fullname" . }}:{{ .Values.service.port }}'] restartPolicy: Never注:configmap 是定义key-value 类型的配置文件,可以自由定义
5)构建多层微服务-系统整体
针对于一个 Chart 进行的,某些复杂的操作可能还需要一些依赖项目,也就是子 Chart,也叫 subcharts。
了解子 Chart 之前,需要了解子 chart 相关的一些信息:
子 chart 是独立的,这意味着子 chart 不能显示依赖其父 chart
所以子 chart 无法访问其父级的值
父 chart 可以覆盖子 chart 的值
Helm 中有可以被所有 charts 访问的全局值的概念
A) 子Charts 放置在charts 文件夹内
B)共享常量与全局常量
共享常量【拷贝】
在“k8sdemo”的“values.yaml”加入下面代码,注意节点的名字必须是子chart名(例如“k8sdemo-backend”)
k8sdemo-backend: replicaCount: 2 k8sdemo-database: replicaCount: 2
在“k8sdemo”的模板里就可以通过“{{ .Values.k8sdemo-database.replicaCount }}” 来访问。当Helm发现节点名是子chart名时,它会自动拷贝这个常量到子chart的“values.yaml”中,因此,在“k8sdemo-database”中,你也可以通过“{{ .Values.replicaCount }}” 来访问这个常量。注意这里并没有包含子chart(“k8sdemo-backend”),而是只有常量名,因为子chart名只是一个标识,而不是常量名的一部分。
全局常量
共享常量只能把常量共享给一个字chart,如果你需要多个子chart之间共享,就需要创建全局常量,它用“global”来标识,下面是示例。
在“k8sdemo-backend”的"values.yaml"中定义:
global: k8sdemoDatabaseService: &k8sdemoDatabaseService k8sdemo-database-service mysqlUserName: dbuser mysqlUserPassword: dbuser mysqlPort: 3306 mysqlHost: *k8sdemoDatabaseService mysqlDatabase: service_config
在“k8sdemo-database”的"values.yaml"中定义:
global: k8sdemoDatabaseService: k8sdemo-database-service mysqlUserName: dbuser mysqlUserPassword: dbuser mysqlRootPassword: root mysqlDatabase: service_config
在“k8sdemo-database”的“deployment.yaml”中引用。
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: {{ .Values.global.mysqlRootPassword }}
- name: MYSQL_USER_NAME
value: {{ .Values.global.mysqlUserName }}
- name: MYSQL_USER_PASSWORD
value: {{ .Values.global.mysqlUserPassword }}
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
value: {{ .Values.global.mysqlDatabase }}C)Chart的依赖关系
我们需要解决问题,例如:十个微服务构成一个Helm 项目如何组合定义Charts 包问题
处理Chart的依赖关系有两种方式:
嵌入式:就是直接把依赖的chart放在“charts”子目录里,这样子chart是父chart的一部分。它是一种紧耦合的关系,好处是比较简单,但不够灵活。
依赖导入式:就是各个chart是并列关系,各自单独调试部署,互相独立,需要合并时再把子chart导入父chart里,它是一种松耦合的关系,好处是比较灵活,但设计更复杂。 在这种结构下,各个chart可以单独工作也可以联合工作。只有需要在chart之间共享的常量才需要在父chart里的"values.yaml"定义,其余的在各自子chart里的"values.yaml"定义就可以了。例如父Charts 可以有dev,uat,pro 三个环境的变量,每次部署可以使用如下命令去覆盖子charts 对应环境变量,而进行不同环境的部署。
helm install --dry-run --values ./k8sdemo/values-dev.yaml --debug k8sdemo ./k8sdemo
发布于 2024-05-30 15:02・IP 属地广东